Posted by Admin on 26-08-2023 in Shiksha hub
Supervisor Maintenance (Infrastructure Equipment), Introduction, Admission, Registration, Eligibility, Duration, Fees, Syllabus 2024
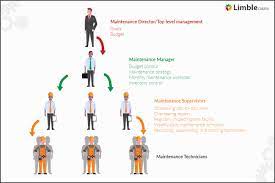
Introduction about SUPERVISOR MAINTENANCE (INFRASTRUCTURE EQUIPMENT)
Supervisor Maintenance, particularly in the realm of infrastructure equipment, plays a vital role in ensuring the seamless operation of various essential systems and facilities. This article delves into the responsibilities, skills, challenges, best practices, and the future of Maintenance Supervisors in the context of infrastructure equipment.
The Role of a Supervisor in Maintenance
Maintenance Supervisors are essential figures in ensuring that infrastructure equipment remains in optimal working condition. They oversee maintenance teams, set priorities, and ensure that tasks are completed efficiently.
Key Responsibilities of a Maintenance Supervisor
Team Leadership: Maintenance Supervisors lead and motivate maintenance teams, ensuring productivity and job satisfaction.
Work Scheduling: They schedule maintenance tasks, preventing downtime and disruptions.
Equipment Inspection: Supervisors regularly inspect equipment to identify issues and plan maintenance accordingly.
Budget Management: They manage maintenance budgets, allocating resources effectively.
Safety Compliance: Ensuring that maintenance activities adhere to safety standards is a crucial responsibility.
Skills and Qualities of an Effective Maintenance Supervisor
An effective Maintenance Supervisor possesses the following skills and qualities:
Technical Knowledge: Understanding of the equipment and systems they oversee.
Communication: Effective communication with team members and superiors.
Problem Solving: Quick and efficient problem-solving abilities.
Leadership: The ability to lead and inspire a team.
Adaptability: Flexibility to handle unexpected issues.
Challenges Faced by Maintenance Supervisors
Maintenance Supervisors encounter various challenges, including:
Aging Infrastructure: Dealing with aging equipment and facilities.
Resource Constraints: Limited budgets and resources.
Regulatory Changes: Staying updated with changing regulations.
Diverse Workforce: Managing teams with diverse skill sets and backgrounds.
Importance of Infrastructure Equipment Maintenance
Effective maintenance of infrastructure equipment is crucial for ensuring the safety, reliability, and longevity of essential systems such as power grids, transportation networks, and water supply systems.
Supervisor Maintenance Best Practices
Regular Equipment Inspection and Preventive Maintenance
Prioritizing Safety in All Maintenance Activities
Continuous Training and Skill Enhancement for the Team
Implementing Maintenance Software for Efficient Management
Training and Development for Maintenance Supervisors
Maintenance Supervisors should undergo training to stay current with industry best practices. Continuous development ensures they can adapt to new technologies and regulatory changes effectively.
Technology and Maintenance Supervision
Technology, such as IoT sensors and predictive maintenance software, is transforming maintenance supervision. It allows for proactive identification of equipment issues, reducing downtime and costs.
The Future of Maintenance Supervision
The future of Maintenance Supervision is likely to be more data-driven and automated, with AI and machine learning playing a significant role in predictive maintenance.
Benefits of Effective Infrastructure Equipment Maintenance
Effective maintenance supervision results in:
Reduced downtime and associated costs
Increased equipment lifespan
Enhanced safety and reliability
Cost-effective resource allocation
Case Study: Successful Maintenance Supervision
Explore a case study highlighting the impact of effective maintenance supervision on an infrastructure project, showcasing real-world results.
Common Myths About Maintenance Supervisors
Debunking common misconceptions and myths about the role and responsibilities of Maintenance Supervisors.
How can I apply for admission to SUPERVISOR MAINTENANCE (INFRASTRUCTURE EQUIPMENT)
Applying for admission to a Supervisor Maintenance program for infrastructure equipment typically involves a specific process that may vary depending on the institution or organization offering the program. Here are the general steps you can follow to apply for admission:
Research and Choose a Program: Begin by researching and identifying institutions or organizations that offer Supervisor Maintenance programs for infrastructure equipment. Ensure that the program aligns with your career goals and interests.
Review Admission Requirements: Visit the program's official website or contact the admissions office to understand the specific admission requirements. These requirements may include educational qualifications, work experience, and other prerequisites.
Prepare Necessary Documents: Gather all the required documents for your application. Common documents may include:
High school diploma or equivalent
Transcripts from previous education (if applicable)
Resume or curriculum vitae highlighting relevant work experience
Letters of recommendation (if required)
Statement of purpose or personal essay
Proof of English language proficiency (for international students)
Complete the Application Form: Most programs have an online application form that you need to fill out. Provide accurate and complete information. Pay close attention to deadlines and submission instructions.
Pay Application Fees: Some programs may require an application fee. Make sure to pay this fee as part of the application process, if applicable.
Submit Transcripts and Documents: Send your transcripts, resume, letters of recommendation, and any other required documents to the institution's admissions office. Ensure that all documents are in order and meet the specified guidelines.
Write a Statement of Purpose: If required, write a compelling statement of purpose. This is an opportunity to explain your interest in the Supervisor Maintenance program and your career aspirations.
Letters of Recommendation: If the program requires letters of recommendation, contact your chosen referees well in advance. Request that they write and submit their letters on time.
English Language Proficiency: If you are an international student and English is not your first language, you may need to demonstrate your proficiency through standardized tests such as TOEFL or IELTS.
Interview (if required): Some programs may require an interview as part of the admission process. Prepare for this interview by reviewing your qualifications and the program's specifics.
Pay Attention to Deadlines: Ensure that you meet all application deadlines. Late applications are often not considered.
Track Your Application: Keep track of your application's progress and follow up with the admissions office if needed.
Wait for Admission Decision: After submitting your application, wait for the institution to review your materials. Admission decisions are typically communicated through email or postal mail.
Acceptance and Enrollment: If you are accepted, you will receive an acceptance letter. Follow the instructions in the letter to confirm your enrollment and complete any additional requirements, such as paying tuition or fees.
What is the eligibility for SUPERVISOR MAINTENANCE (INFRASTRUCTURE EQUIPMENT)
Eligibility criteria for a Supervisor Maintenance program in infrastructure equipment can vary depending on the institution or organization offering the program. However, I can provide you with a general idea of the common eligibility requirements that are typically expected for such programs:
Educational Qualifications:
High School Diploma or Equivalent: Many programs require applicants to have a high school diploma or its equivalent. Some programs may require a specific level of academic achievement.
Bachelor's Degree (in some cases): Some Supervisor Maintenance programs may be designed for individuals who already hold a bachelor's degree, especially if the program is at the postgraduate level.
Work Experience:
Relevant Work Experience: Many Supervisor Maintenance programs, especially those at the postgraduate level, may prefer applicants with prior work experience in maintenance, engineering, or a related field. The required years of experience can vary, but it is often in the range of 1-5 years.
English Language Proficiency (for International Students):
If you are an international student and English is not your first language, you may be required to demonstrate English language proficiency through standardized tests like TOEFL or IELTS. Each program sets its own required scores.
Letters of Recommendation:
Some programs may request letters of recommendation from individuals who can speak to your qualifications and readiness for the program. Typically, two to three letters are required.
Statement of Purpose or Personal Essay:
A statement of purpose or personal essay may be required to assess your motivation, goals, and suitability for the program. It provides an opportunity to explain why you want to pursue a career in Supervisor Maintenance.
Interview (if required):
Certain programs may conduct interviews as part of the admission process to further assess your qualifications and potential for success in the program.
Other Requirements:
Some programs may have specific prerequisites or additional requirements, such as specific coursework, certifications, or licenses.
How long does it takes to complete a SUPERVISOR MAINTENANCE (INFRASTRUCTURE EQUIPMENT)
The duration to complete a Supervisor Maintenance program in infrastructure equipment can vary based on several factors, including the level of the program, the specific institution or organization offering it, and whether it's a full-time or part-time program. Here's a general overview of the typical timeframes for different levels of Supervisor Maintenance programs:
Certificate or Diploma Programs:
Certificate programs in Supervisor Maintenance may take anywhere from a few weeks to a few months to complete.
Diploma programs can take around 6 months to 1 year.
Associate's Degree Programs:
Associate's degree programs in Supervisor Maintenance usually take about 2 years to complete when pursued on a full-time basis.
Bachelor's Degree Programs:
If you opt for a Bachelor's degree in Supervisor Maintenance, it typically takes around 4 years to complete. Some programs may offer accelerated options, and the duration can vary depending on your course load.
Master's Degree Programs:
Master's programs in Supervisor Maintenance, if available, usually take 1 to 2 years to complete. The duration may vary based on whether you are pursuing a full-time or part-time program.
Ph.D. or Doctoral Programs:
Doctoral programs in this field, if offered, can take 3 to 5 years or longer to complete, depending on the research and dissertation requirements.
What are potential career opportunities after SUPERVISOR MAINTENANCE (INFRASTRUCTURE EQUIPMENT)
Completing a Supervisor Maintenance program in infrastructure equipment can open up various career opportunities in both public and private sectors. Here are some potential career paths and opportunities that you can pursue after obtaining qualifications in this field:
Maintenance Supervisor: As the most direct career path, you can work as a Maintenance Supervisor overseeing the maintenance and repair of infrastructure equipment, such as machinery, electrical systems, or facilities. You'll be responsible for managing maintenance teams and ensuring equipment remains in optimal working condition.
Facility Manager: Facility managers are responsible for the overall maintenance and operation of buildings, grounds, and associated infrastructure. This role may involve overseeing a wide range of maintenance activities, from HVAC systems to security systems.
Maintenance Manager: A Maintenance Manager typically oversees maintenance operations within an organization, ensuring that equipment and facilities are properly maintained. This role often involves strategic planning, budget management, and team leadership.
Maintenance Engineer: Maintenance engineers are responsible for designing and implementing maintenance programs and strategies. They work on improving the reliability and performance of infrastructure equipment.
Project Manager: With experience, you can transition into a role as a Project Manager, overseeing maintenance and renovation projects. This role involves budgeting, planning, and coordinating the activities of maintenance teams.
Infrastructure Analyst: Infrastructure analysts assess the condition of infrastructure equipment and develop maintenance plans to ensure efficient operation. They may work for consulting firms, government agencies, or private companies.
Operations Manager: Operations managers oversee day-to-day operations in various industries, including manufacturing and logistics. Maintenance plays a critical role in these sectors, and your expertise in Supervisor Maintenance can be valuable.
Quality Assurance Manager: Quality assurance managers ensure that maintenance and repair processes meet quality standards and compliance requirements. They are responsible for quality control and process improvement.
Energy Manager: Energy managers focus on optimizing energy consumption in facilities and infrastructure. They implement energy-efficient maintenance practices to reduce costs and environmental impact.
Consultant: As a maintenance consultant, you can offer your expertise to organizations looking to improve their maintenance practices. You may provide advice on best practices, process optimization, and cost-saving strategies.
Government Positions: Many government agencies at the local, state, and federal levels hire Maintenance Supervisors and related professionals to maintain public infrastructure, such as roads, bridges, and utilities.
Asset Management Specialist: Asset management specialists are responsible for managing an organization's physical assets, including infrastructure equipment. They ensure that assets are used efficiently and effectively.
Equipment Manufacturer: You can work for companies that manufacture infrastructure equipment, providing technical support and maintenance guidance to customers who use their products.
Health and Safety Manager: In organizations with a strong focus on safety, you can work as a health and safety manager, ensuring that maintenance activities adhere to safety standards and regulations.
Entrepreneurship: You might consider starting your own maintenance services business, offering maintenance and repair services to various clients and industries.
Syllabus of SUPERVISOR MAINTENANCE (INFRASTRUCTURE EQUIPMENT)
The syllabus for a Supervisor Maintenance program in infrastructure equipment can vary depending on the institution and the specific curriculum they offer. However, I can provide a general overview of the topics and subjects that are often covered in such programs, typically divided into semesters. Please note that the specific courses and their sequencing may differ from one program to another. Here's a semester-wise breakdown of a potential syllabus:
Semester 1:
Introduction to Maintenance Supervision
Role and responsibilities of a Maintenance Supervisor
Importance of maintenance in infrastructure
Basic Engineering Concepts
Understanding infrastructure equipment
Equipment operation and maintenance basics
Safety in Maintenance
Occupational safety and health regulations
Developing safety protocols for maintenance activities
Maintenance Planning and Scheduling
Maintenance planning techniques
Developing maintenance schedules
Semester 2:
Technical Skills for Maintenance
Electrical systems maintenance
Mechanical systems maintenance
HVAC and plumbing maintenance
Maintenance Management Software
Introduction to computerized maintenance management systems (CMMS)
Utilizing CMMS for maintenance planning and tracking
Team Leadership and Communication
Effective leadership in maintenance
Communication skills for managing maintenance teams
Budgeting and Resource Management
Budgeting for maintenance projects
Resource allocation and procurement
Semester 3:
Predictive and Preventive Maintenance
Implementing predictive maintenance techniques
Developing preventive maintenance strategies
Regulatory Compliance and Environmental Considerations
Compliance with maintenance regulations and standards
Environmental impact and sustainability in maintenance
Maintenance Troubleshooting
Identifying and resolving equipment issues
Root cause analysis and failure modes
Facility Management
Facility maintenance and operations
Space planning and utilization
Semester 4:
Project Management for Maintenance
Project planning and execution
Project management tools and techniques
Advanced Maintenance Technologies
Internet of Things (IoT) in maintenance
Predictive maintenance using data analytics
Quality Control and Assurance
Quality standards and control measures in maintenance
Continuous improvement in maintenance processes
Capstone Project
A practical project involving real-world maintenance scenarios
Internship opportunities after completing SUPERVISOR MAINTENANCE (INFRASTRUCTURE EQUIPMENT)
After completing a Supervisor Maintenance program in infrastructure equipment, there are several internship opportunities that can provide valuable hands-on experience and further enhance your skills and knowledge. Internships can be a stepping stone to a successful career in this field. Here are some potential internship opportunities:
Maintenance Supervisor Intern:
Work as an intern under the supervision of an experienced Maintenance Supervisor to gain insights into the day-to-day responsibilities of managing maintenance teams, equipment, and facilities.
Facility Management Intern:
Intern with a facility management company or organization to learn about overseeing the maintenance and operation of buildings, grounds, and infrastructure systems.
Maintenance Engineering Intern:
Gain experience as an intern in maintenance engineering, where you can apply your knowledge to address technical challenges and optimize maintenance processes.
Maintenance Planning Intern:
Work with a maintenance planning and scheduling team to understand how maintenance tasks are organized, scheduled, and tracked for efficiency.
Equipment Manufacturer Intern:
Intern with a company that manufactures infrastructure equipment to learn about the design, maintenance, and servicing of specific types of equipment.
Energy Management Intern:
Intern with organizations or energy management firms to focus on optimizing energy consumption through effective maintenance practices.
Maintenance Software Intern:
Join a company that develops or utilizes computerized maintenance management systems (CMMS) to learn about the technology and tools used for maintenance planning and tracking.
Government Agency Intern:
Explore internship opportunities with government agencies responsible for maintaining public infrastructure, such as transportation departments or public works.
Quality Assurance and Compliance Intern:
Intern with organizations that emphasize quality control and regulatory compliance in maintenance activities.
Project Management Intern:
Work with a project management team that oversees maintenance and renovation projects, gaining exposure to project planning and execution.
Health and Safety Intern:
Intern with organizations that prioritize safety in maintenance activities to learn about safety protocols and regulations.
Consulting Intern:
Intern with maintenance consulting firms to gain experience in providing maintenance best practices and recommendations to clients.
Nonprofit Organizations and NGOs:
Some nonprofit organizations and NGOs work on infrastructure projects in developing regions. Interning with such organizations can provide unique experience and contribute to social causes.
Customized Internships:
Seek out customized internships that align with your specific interests and career goals. Some organizations may offer tailored internship opportunities in specialized areas of maintenance.
Scholarship and grants for SUPERVISOR MAINTENANCE (INFRASTRUCTURE EQUIPMENT)
Scholarships and grants can provide financial assistance to students pursuing a Supervisor Maintenance program in infrastructure equipment. These opportunities can help cover tuition, fees, and related educational expenses. Here are some potential sources of scholarships and grants:
Institutional Scholarships: Many universities and colleges offer scholarships specifically for students enrolled in maintenance and infrastructure-related programs. Check with the financial aid office of your institution for information on available scholarships.
Professional Associations: Industry-specific organizations and associations may offer scholarships to students pursuing careers in maintenance and infrastructure. For example, the American Society of Civil Engineers (ASCE) or the Association for Facilities Engineering (AFE) might have scholarship programs.
Government Scholarships and Grants: Government agencies may provide scholarships or grants to individuals studying fields related to infrastructure maintenance. Check with federal, state, or local government websites for information on available opportunities.
Private Foundations and Nonprofits: Some private foundations and nonprofit organizations offer scholarships and grants for students pursuing careers in maintenance and infrastructure. Research organizations related to your field of study to identify potential opportunities.
Corporate Sponsorships: Some companies offer scholarship programs for students in return for a commitment to work for the company for a specified period after graduation. These are often available in industries where skilled maintenance professionals are in high demand.
Trade Unions and Labor Organizations: Trade unions and labor organizations may have scholarship programs for individuals pursuing careers in maintenance, particularly in trades like electrical, HVAC, and construction.
Military Scholarships: If you have a military background or are a veteran, you may be eligible for scholarships and grants through military-related programs, such as the GI Bill.
Merit-Based Scholarships: Many scholarships are awarded based on academic achievements, leadership, and other accomplishments. While not specific to maintenance, your academic performance can help you qualify for these scholarships.
Need-Based Scholarships: Scholarships based on financial need can assist students who may have limited financial resources to pursue their education. These scholarships are typically awarded through the institution's financial aid office.
Online Scholarship Databases: Websites like Fastweb, Scholarships.com, and Cappex provide databases of scholarships that you can search based on your field of study and other criteria.
Community and Civic Organizations: Local community groups, such as Rotary Clubs, may offer scholarships to students in their area pursuing education in infrastructure maintenance.
Essay and Video Contests: Some organizations host contests that require essays or videos related to infrastructure or maintenance topics, with cash prizes or scholarships for the winners.
Conclusion
Maintenance Supervisors in infrastructure equipment are crucial for the smooth functioning of essential systems. Their roles continue to evolve as technology and regulatory requirements change. As we move into an increasingly automated future, the importance of skilled and adaptable Maintenance Supervisors becomes even more pronounced.
FAQ,s
What is the role of a Maintenance Supervisor in infrastructure equipment maintenance?
A Maintenance Supervisor is responsible for overseeing maintenance teams, ensuring that equipment and facilities are properly maintained, and managing maintenance operations efficiently.
What qualifications are required to become a Maintenance Supervisor?
Qualifications typically include a relevant educational background, such as a degree in engineering or a related field, along with several years of practical experience in maintenance or a related role.
What skills are essential for a Maintenance Supervisor?
Key skills include technical knowledge, leadership, communication, problem-solving, and adaptability.
What are some challenges faced by Maintenance Supervisors in infrastructure maintenance?
Maintenance Supervisors often deal with aging infrastructure, limited budgets, regulatory changes, and the management of diverse maintenance teams.
How does technology impact Maintenance Supervision?
Technology, such as IoT sensors and predictive maintenance software, is transforming the field by allowing for proactive identification of equipment issues and reducing downtime.
What is the future of Maintenance Supervision in infrastructure equipment?
The future is expected to be more data-driven and automated, with AI and machine learning playing a significant role in predictive maintenance.
What are the benefits of effective infrastructure equipment maintenance?
Effective maintenance results in reduced downtime and associated costs, increased equipment lifespan, enhanced safety and reliability, and cost-effective resource allocation.
Can I specialize in a specific type of infrastructure equipment maintenance?
Yes, you can specialize in areas such as electrical systems, HVAC, industrial machinery, or specific types of infrastructure, depending on your interests and career goals.
Are there opportunities for advancement in a Maintenance Supervisor career?
Yes, with experience, Maintenance Supervisors can advance to higher-level positions, such as Maintenance Manager, Facility Manager, or Project Manager.
How can I gain practical experience in maintenance before becoming a Maintenance Supervisor?
Consider internships, cooperative education programs, or entry-level positions in maintenance to gain hands-on experience and build your skills.
What are the safety considerations in infrastructure equipment maintenance?
Safety is a top priority in maintenance. Maintenance professionals should adhere to safety protocols, wear appropriate personal protective equipment, and undergo safety training.
Are there professional certifications available for Maintenance Supervisors?
Yes, there are certifications, such as Certified Maintenance and Reliability Professional (CMRP), that can enhance your credentials and career prospects.
How can I stay updated with the latest developments in maintenance technology and best practices?
Join professional associations, attend industry conferences, and participate in continuing education and training programs to stay current in the field.
What is the average salary for Maintenance Supervisors in infrastructure maintenance?
Salary can vary based on factors like location, experience, and the specific industry, but the average salary for Maintenance Supervisors is competitive.
Can I pursue a Supervisor Maintenance program online or part-time?
Many institutions offer flexible options, including online and part-time programs, to accommodate the needs of working professionals and students.