Posted by Admin on 02-11-2022 in Shiksha hub
Ph.D. in Arthroplasty Introduction Admission Registration, Eligibility, Duration, Fees, Syllabus 2024
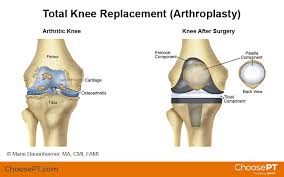
Introduction about Ph.D. in Arthroplasty
Arthroplasty, often referred to as joint replacement surgery, is a medical procedure aimed at restoring the function and alleviating pain in damaged or degenerated joints. It involves the surgical removal of the damaged joint and its replacement with a prosthetic implant, which can be made of various materials, including metal, plastic, or ceramic.
This procedure is commonly performed on major weight-bearing joints like the hip and knee, as well as other joints such as the shoulder, elbow, and ankle. Arthroplasty is typically recommended for individuals who suffer from severe joint conditions, such as osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, or other degenerative joint diseases that result in chronic pain, limited mobility, and a diminished quality of life.
The primary goals of arthroplasty are to reduce pain, improve joint function, and enhance the patient's overall quality of life. It has proven to be a highly effective and successful method for restoring mobility and relieving discomfort in patients who have exhausted non-surgical treatments like physical therapy and medication.
There are different types of arthroplasty, each tailored to the specific joint being treated and the patient's unique needs. Hip and knee replacements are among the most common forms of arthroplasty, and these surgeries have brought about significant improvements in the lives of countless individuals worldwide.
As medical technology continues to advance, arthroplasty procedures have become safer, more reliable, and associated with shorter recovery times. It has become a vital tool in the field of orthopedic surgery, offering hope and relief to those who suffer from debilitating joint conditions.
How can I apply for admission to Ph.D. in Arthoplasty Program
Applying for admission to a Ph.D. program in Arthroplasty or any related field generally involves several key steps. Here's a general outline of the process:
Research Programs: Start by researching Ph.D. programs in Arthroplasty or Orthopedic Surgery at various universities. Look for programs that align with your research interests and career goals.
Meet Admission Requirements: Ensure you meet the admission requirements, which typically include a master's degree in a related field (e.g., orthopedic surgery, biomechanics), academic transcripts, and specific prerequisite courses.
Prepare Application Materials:
Curriculum Vitae (CV): Create a detailed CV that highlights your academic and research achievements, relevant work experience, and publications.
Statement of Purpose: Write a compelling statement of purpose that outlines your research interests, career goals, and why you're interested in pursuing a Ph.D. in Arthroplasty.
Letters of Recommendation: Request letters of recommendation from professors or professionals who can attest to your academic and research abilities.
Academic Transcripts: Prepare and provide transcripts from your previous academic institutions.
Test Scores: Some programs may require standardized test scores, such as the GRE (Graduate Record Examination). Check the specific requirements of the programs you're applying to.
Identify Potential Advisors: If you have a specific research interest within arthroplasty, identify potential advisors whose expertise aligns with your interests. Reach out to them to express your interest and seek their guidance.
Application Submission: Complete the online application for the Ph.D. program of your choice. Pay attention to application deadlines, as they vary by institution. Submit all required materials through the university's application portal.
Interview: If your application is shortlisted, you may be invited for an interview, which could be conducted in person or via video conferencing. Be prepared to discuss your research interests and academic background.
Financial Aid and Scholarships: Explore funding opportunities, including scholarships, grants, and assistantships, which can help cover tuition and living expenses during your Ph.D. studies.
Acceptance and Enrollment: Once you receive an offer of admission, carefully review the terms and conditions. If you decide to accept the offer, follow the enrollment procedures outlined by the university.
Visa and Immigration (International Students): If you are an international student, you will need to apply for a student visa and meet the immigration requirements of the country where you will be studying.
It's important to note that admission requirements and procedures may vary between universities and countries. Therefore, it's crucial to thoroughly research the specific Ph.D. programs you're interested in and follow their application guidelines closely. Additionally, reaching out to the program coordinators or admissions offices for clarification on any doubts or questions can be beneficial during the application process.
What is the eligibility for Ph.D. in Arthroplasty
The eligibility requirements for a Ph.D. in Arthroplasty or a related field can vary from one university to another, and they depend on the specific program's admission criteria. However, I can provide you with a general idea of the typical eligibility criteria for pursuing a Ph.D. in Arthroplasty:
Educational Background: You will generally need a strong academic foundation, which often includes:
A master's degree in a related field, such as orthopedic surgery, biomechanics, biomedical engineering, or a closely related discipline. Some programs may accept candidates with a bachelor's degree, but a master's degree is more common.
Academic Transcripts: You will be required to provide academic transcripts from your previous institutions to demonstrate your academic performance.
Standardized Test Scores: Some universities may require standardized test scores as part of the application, such as the GRE (Graduate Record Examination) or equivalent tests. Check the specific requirements of the programs you are interested in.
Statement of Purpose (SOP): You'll need to submit a well-written SOP that outlines your research interests, career goals, and why you wish to pursue a Ph.D. in Arthroplasty. This document should demonstrate your motivation and fit with the program.
Letters of Recommendation: You'll typically need to provide letters of recommendation from professors or professionals who can speak to your academic and research potential. These letters should support your application and highlight your qualifications.
Research Experience: Having prior research experience in a relevant field can be a significant advantage. Be prepared to showcase any research projects, publications, or presentations you've been involved in.
Interview (Possibly): Some programs may require an interview as part of the admission process. During the interview, you may discuss your research interests and clarify any questions the admissions committee may have.
Language Proficiency: If you're not a native English speaker and your education was not primarily conducted in English, you may need to provide English language proficiency test scores, such as TOEFL or IELTS.
Specific Prerequisite Courses: Some programs may have specific prerequisite coursework requirements, especially if your academic background is not directly related to arthroplasty or orthopedics. You might need to complete certain courses to bridge any knowledge gaps.
It's essential to research the admission requirements of the specific Ph.D. programs you are interested in, as these criteria can vary between universities. Admission to Ph.D. programs in highly specialized fields like Arthroplasty can be competitive, so it's advisable to reach out to the program coordinators or admissions offices for clarification and guidance on the specific requirements for each program you're considering.
How long does it takes to complete a Ph.D. in Arthroplasty program
The duration of a Ph.D. program in Arthroplasty, as with Ph.D. programs in many other fields, can vary depending on several factors. On average, a Ph.D. program typically takes about 4 to 6 years to complete, but this time frame can be influenced by the following factors:
Research Progress: The primary component of a Ph.D. program is original research. The time it takes to complete your research and dissertation can vary significantly based on the complexity of your project, the availability of resources, and your own research progress.
Program Structure: Some universities offer structured Ph.D. programs with a set timeline for coursework, qualifying exams, and dissertation completion. Others may provide more flexibility, allowing you to progress at your own pace.
Funding: The availability of funding, such as research grants, assistantships, and scholarships, can impact the time it takes to complete your Ph.D. Full funding can enable you to focus on your research without the need for additional work commitments.
Advisor and Committee: Your relationship with your research advisor and dissertation committee plays a crucial role. Effective guidance and collaboration can expedite your research progress and dissertation writing.
Publication Requirements: Some programs may have publication requirements, meaning you need to publish your research in peer-reviewed journals before completing your Ph.D. This can extend the time needed for completion.
Teaching or Assistantship Obligations: If you have teaching or research assistantship responsibilities, this may reduce the time you can devote to your research, potentially extending your program's duration.
Qualifying Exams: The timing and success of your qualifying exams can affect your progress. Some students may require additional preparation and attempts.
Dissertation Writing and Defense: The process of writing your dissertation and scheduling a successful defense can take a significant amount of time. This stage may vary in duration depending on the complexity and quality of your research.
Personal Factors: Your own commitment, work habits, and ability to balance research with other responsibilities can influence how long it takes to complete your Ph.D.
It's important to discuss the specific timeline and expectations with your academic advisor and program coordinators, as different universities and departments may have varying requirements and structures for their Ph.D. programs. Additionally, regularly reviewing and updating your progress toward your degree milestones can help you stay on track and complete your Ph.D. in a reasonable amount of time.
What are potential career opportunities after Ph.D. in Arthroplasty
Earning a Ph.D. in Arthroplasty opens up a range of career opportunities in both academic and non-academic settings. Here are some potential career paths for individuals with a Ph.D. in Arthroplasty:
Academic Research and Teaching: Many Ph.D. graduates choose to pursue careers in academia. They can become professors or researchers at universities and colleges, where they teach students, conduct research, and contribute to the academic community through publications.
Clinical Research: Ph.D. graduates in Arthroplasty can work in clinical research settings, collaborating with healthcare institutions or research organizations. They may design and conduct clinical trials, analyze data, and contribute to advancements in arthroplasty techniques and technology.
Orthopedic Surgeon: While a Ph.D. is not a medical degree, some individuals with a Ph.D. in Arthroplasty choose to pursue medical training after their doctorate and become orthopedic surgeons. This combination of expertise can be valuable in providing comprehensive patient care.
Biomechanical Engineer: Arthroplasty researchers can work in the field of biomechanical engineering, developing and improving prosthetic joint devices. They may collaborate with medical device companies, hospitals, or research institutions.
Medical Device Industry: Graduates can join the medical device industry as product managers, research scientists, or engineers. They may be involved in designing, testing, and marketing orthopedic implants and devices.
Consulting: Ph.D. holders can work as consultants, providing expert advice to healthcare organizations, medical device companies, or government agencies on matters related to arthroplasty, joint replacement procedures, and patient care.
Healthcare Administration: Some graduates choose to enter healthcare administration roles, such as hospital administrators or healthcare policy analysts, where they can use their expertise to improve patient care and the delivery of orthopedic services.
Government and Regulatory Agencies: Employment opportunities are available in government agencies and regulatory bodies, where individuals with expertise in arthroplasty can contribute to the development of policies and regulations related to orthopedic procedures and devices.
Nonprofit Organizations: Some graduates may work with nonprofit organizations focused on improving musculoskeletal health and orthopedic care, participating in research, advocacy, and community outreach.
Private Practice: Ph.D. holders with a strong clinical background can open their own orthopedic practice or work in private clinics, specializing in arthroplasty and joint replacement procedures.
Rehabilitation and Physical Therapy: Individuals with a Ph.D. in Arthroplasty may collaborate with physical therapists and rehabilitation professionals to develop and implement post-operative rehabilitation protocols.
Healthcare Research and Policy Analysis: Graduates can work in healthcare research and policy organizations, studying the effectiveness of arthroplasty procedures, healthcare outcomes, and healthcare policy.
Global Health and Humanitarian Work: Some individuals use their expertise to contribute to global health initiatives, working with international organizations to improve orthopedic care in underserved regions.
The career path you choose after earning a Ph.D. in Arthroplasty may depend on your specific interests, expertise, and the opportunities available in your chosen field. It's essential to network with professionals in your desired area and stay updated on developments in the field to make informed decisions about your career path.
Syllabus of Ph.D. in Arthroplasty
The specific syllabus for a Ph.D. in Arthroplasty can vary significantly between universities and programs. The coursework and research requirements are often tailored to the individual student's research interests and the focus of the program. However, I can provide a general outline of what a semester-wise syllabus might look like for a Ph.D. in Arthroplasty:
Please note that this is a general overview and the actual courses and research topics will depend on the program and your chosen research area.
Semester 1:
Research Methodology:
Introduction to research design and methodologies.
Data collection and analysis techniques.
Ethical considerations in research.
Advanced Topics in Arthroplasty:
In-depth study of arthroplasty techniques and technologies.
Review of current research in the field.
Biomechanics:
Study of the mechanical behavior of the musculoskeletal system.
Application of biomechanical principles to arthroplasty.
Semester 2:
Advanced Biostatistics:
Statistical methods for analyzing medical data.
Application of statistical tools to arthroplasty research.
Literature Review and Proposal Development:
Review of relevant literature in the field.
Development of a research proposal for the Ph.D. dissertation.
Clinical Observations:
Observations in clinical settings, including surgeries and patient care.
Semester 3:
Dissertation Research I:
Initiation of original research work.
Data collection and analysis.
Regular meetings with the research advisor.
Specialized Elective Course:
Depending on your research focus, you may take an elective course in areas like orthopedic surgery, materials science, or medical imaging.
Semester 4:
Dissertation Research II:
Continued research and data collection.
Begin drafting the dissertation.
Research Seminar:
Present your research findings to peers and faculty.
Receive feedback and refine your research.
Semester 5:
Dissertation Writing:
Concentrate on writing the dissertation.
Regular meetings with the dissertation committee for guidance.
Semester 6:
Dissertation Defense:
Defend your research before a dissertation committee.
Address questions and revisions.
Please keep in mind that this is a general template and can vary based on the program, university, and your specific research interests. Ph.D. programs in Arthroplasty often prioritize research, so the majority of your time and effort will be dedicated to your original research work, culminating in the completion and defense of your dissertation. It's essential to consult with your academic advisor and program coordinator to get the most accurate and up-to-date information on the specific requirements and syllabus for your Ph.D. program.
Internship opportunities after completing Ph.D. in Arthoplasty
After completing a Ph.D. in Arthroplasty, you may have the opportunity to pursue various internship and post-doctoral positions to further enhance your skills and gain practical experience. These internships can provide valuable insights and help you transition into the workforce. Here are some internship opportunities you can consider:
Post-Doctoral Research Fellowships: Many universities and research institutions offer post-doctoral positions for Ph.D. graduates. These positions involve conducting advanced research, often under the guidance of a senior researcher. It's an excellent way to deepen your research expertise and build your academic and publication record.
Clinical Fellowships: If your Ph.D. research focused on clinical aspects of arthroplasty, you can seek clinical fellowships at hospitals or medical centers. These fellowships provide hands-on experience in patient care, surgeries, and post-operative management.
Medical Device Industry Internships: Companies in the medical device industry, particularly those specializing in orthopedic implants and arthroplasty technologies, may offer internships. These positions could involve product development, quality control, regulatory affairs, or clinical trials.
Biomechanics Research Internships: Internships in research organizations or companies focusing on biomechanics can help you apply your knowledge to the development of prosthetic joint devices and their biomechanical analysis.
Healthcare Administration and Policy Internships: If you are interested in healthcare policy, you can intern with government agencies, nonprofit organizations, or healthcare consulting firms to gain insights into healthcare administration, policy analysis, and healthcare economics.
Rehabilitation and Physical Therapy Internships: Consider internships in rehabilitation centers or physical therapy clinics, where you can work with physical therapists and rehabilitation specialists to gain practical experience in post-operative care and rehabilitation protocols.
Global Health Initiatives: Engage in international internships with organizations working on global health and humanitarian projects related to orthopedic care, joint replacement, and musculoskeletal health.
Teaching and Academic Internships: If you are interested in academia, you can seek teaching or research internships at universities or colleges. These positions can help you gain experience in curriculum development, lecturing, and academic research.
Consulting Internships: Consulting firms specializing in healthcare, orthopedics, or medical devices may offer internships where you can apply your expertise to solve real-world problems and provide consultancy to clients.
Patient Advocacy and Support: Some organizations and foundations focused on musculoskeletal health and arthroplasty patient support may offer internships that involve working closely with patients, educating them, and providing support services.
It's important to proactively seek out internship opportunities that align with your career goals and interests. Networking with professionals in your field, staying updated on job postings, and leveraging your academic advisors can be valuable in finding the right internship positions. Internships can serve as a stepping stone to your desired career path and provide you with practical experience and networking opportunities.
Scholarship and grants for Ph.D. in Arthroplasty
Pursuing a Ph.D. in Arthroplasty can be a substantial financial commitment, but there are various scholarship and grant opportunities available to help support your academic and research endeavors. These funding options can help cover tuition, living expenses, and research costs. Here are some potential sources of financial aid:
University-Specific Scholarships: Many universities offer scholarships and fellowships to Ph.D. students based on academic merit and research potential. Check with the universities you're interested in for details on these opportunities.
Government Grants: Government agencies, such as the National Institutes of Health (NIH) in the United States, may provide research grants and fellowships to support doctoral research in areas related to arthroplasty and orthopedics.
Professional Organizations: Organizations like the Orthopaedic Research and Education Foundation (OREF) and the American Association of Hip and Knee Surgeons (AAHKS) offer research grants and scholarships to students and professionals in the field of arthroplasty.
Private Foundations and Endowments: There are numerous private foundations and endowments that provide scholarships and grants for students pursuing research in orthopedics and arthroplasty. Examples include the Arthritis Foundation and the American Orthopaedic Association.
Industry and Corporate Funding: Medical device companies and orthopedic implant manufacturers may offer research grants or sponsorships to Ph.D. students conducting research related to their products or technologies.
Fulbright Program: If you are an international student looking to study in the United States, the Fulbright Program offers scholarships for foreign students to pursue Ph.D. studies in various fields, including arthroplasty.
Disease-Specific Foundations: Some foundations focus on specific musculoskeletal diseases, such as osteoarthritis. They may offer research funding or scholarships for students studying these conditions.
Nonprofit Organizations: Various nonprofit organizations may provide scholarships or grants to students interested in arthroplasty research, especially those who demonstrate a commitment to improving patient care and outcomes.
Minority and Diversity Scholarships: Some organizations and institutions offer scholarships to underrepresented minority students pursuing advanced degrees in healthcare and related fields.
Institutional Funding: Some academic departments and colleges within universities may have their own funds or scholarships specifically for doctoral students pursuing research in arthroplasty.
When applying for scholarships and grants, make sure to review the eligibility criteria, deadlines, and application requirements carefully. Prepare a compelling application that showcases your academic achievements, research potential, and commitment to advancing the field of arthroplasty. Additionally, consider reaching out to professors and advisors for guidance and potential funding opportunities within your academic institution.
FAQ's
Certainly, here are some frequently asked questions (FAQs) related to pursuing a Ph.D. in Arthroplasty:
What is Arthroplasty? Arthroplasty is a surgical procedure that involves the replacement of a damaged or arthritic joint with a prosthetic implant. It is often used to alleviate pain and improve joint function.
How long does it take to complete a Ph.D. in Arthroplasty? The duration of a Ph.D. program varies, but it typically takes around 4 to 6 years to complete, depending on factors like research progress and program structure.
What are the eligibility requirements for a Ph.D. in Arthroplasty? Eligibility requirements generally include a master's degree in a related field, academic transcripts, standardized test scores (if required), a statement of purpose, letters of recommendation, and, in some cases, specific prerequisite courses.
What are the career opportunities after completing a Ph.D. in Arthroplasty? Career opportunities include academia, clinical research, orthopedic surgery, biomechanical engineering, medical device industry, healthcare administration, consulting, and more.
Can I work as an orthopedic surgeon with a Ph.D. in Arthroplasty? While a Ph.D. provides in-depth knowledge in the field, it is not a medical degree. To become an orthopedic surgeon, you typically need to complete medical school and an orthopedic residency.
What is the typical curriculum for a Ph.D. in Arthroplasty? The curriculum can vary, but it often includes courses in research methodology, advanced topics in arthroplasty, biomechanics, and specialized elective courses. The focus is on research and the completion of a dissertation.
Are there internship opportunities after completing a Ph.D. in Arthroplasty? Yes, graduates can pursue post-doctoral research fellowships, clinical fellowships, internships in the medical device industry, biomechanics research internships, healthcare administration internships, and more.
What scholarships and grants are available for Ph.D. students in Arthroplasty? Scholarships and grants can come from universities, government agencies, professional organizations, private foundations, industry sponsors, and more. These sources can help cover tuition and research expenses.
How can I find a Ph.D. program in Arthroplasty? You can search for Ph.D. programs in Arthroplasty at universities and research institutions. Start by reviewing university websites, contacting program coordinators, and exploring research areas that align with your interests.
What is the expected salary for Ph.D. graduates in Arthroplasty-related fields? Salary can vary widely depending on the specific career path. Professors in academia, for instance, can earn differently than researchers in the medical device industry or orthopedic surgeons. Salaries are often influenced by location, experience, and job responsibilities.
Remember that specific details may vary depending on the university, country, and program, so it's essential to research individual programs and consult with academic advisors for the most accurate information.
Conclusion
Ph.D. programs in highly specialized fields like Arthroplasty can be competitive, so it's advisable to reach out to the program coordinators or admissions offices for clarification and guidance on the specific requirements for each program you're considering.