Posted by Admin on 29-08-2023 in Shiksha hub
Mechatronics in Charge, Introduction, Admission, Registration, Eligibility, Duration, Fees, Syllabus 2024
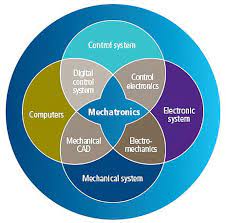
Introduction about MECHATRONICS IN CHARGE
Mechatronics, a term coined by the Japanese engineer Ko Kikuchi in the 1960s, represents a dynamic and interdisciplinary field that combines elements of mechanical engineering, electronics, computer science, and control engineering. Mechatronics is a fusion of technologies aimed at creating intelligent systems, leading to the birth of 'Mechatronics in Charge.' In this article, we will explore the world of Mechatronics in Charge, understand its significance in modern industries, and delve into its diverse applications.
What Is Mechatronics in Charge?
Mechatronics in Charge refers to the integration of mechatronics principles and technologies in various industrial processes and systems. It involves the smart utilization of mechanical components, electrical circuits, and electronic systems to control, monitor, and optimize complex machinery and processes. This innovative approach allows machines and systems to operate efficiently, with a high degree of automation and intelligence.
The Role of Mechatronics in Modern Industries
Mechatronics in Charge plays a pivotal role in modern industries, revolutionizing the way operations are conducted. Whether it's in manufacturing, automotive, robotics, or even aerospace, mechatronics has become an indispensable part of industrial processes. It ensures higher precision, reliability, and productivity, making industries more competitive and sustainable.
Key Components of Mechatronics Systems
To comprehend Mechatronics in Charge, it's essential to understand the fundamental components that make up mechatronics systems.
Mechanical Components
Mechanical components include various parts such as sensors, actuators, and mechanical structures. Sensors detect physical changes and provide data to the system, while actuators are responsible for executing actions based on the received data.
Electrical Components
Electrical components encompass circuits and wiring, enabling the flow of electricity within the system. These components are crucial for the transmission of control signals and data.
Electronic Components
Electronic components, such as microcontrollers and processors, are the brain of mechatronics systems. They process data, make decisions, and control the overall operation of the system.
The Importance of Interdisciplinary Knowledge
Mechatronics in Charge demands interdisciplinary knowledge. Professionals working in this field need to have expertise in mechanical engineering, electronics, computer programming, and control systems. This diverse skill set is crucial for designing, implementing, and maintaining mechatronics systems effectively.
Applications of Mechatronics in Charge
Mechatronics in Charge has far-reaching applications in various sectors. Here are some examples:
Mechatronics in Charge in Automotive Industry
In the automotive industry, mechatronics systems control various functions, including engine performance, safety features, and entertainment systems. These systems ensure a smoother and safer driving experience.
Mechatronics in Charge in Manufacturing
In manufacturing, mechatronics is used for process automation, quality control, and production efficiency. It plays a critical role in creating smart factories of the future.
Mechatronics in Charge in Robotics
Robotics heavily relies on mechatronics. Mechatronics systems are responsible for the precision and adaptability of robots in tasks ranging from surgery to space exploration.
Benefits of Implementing Mechatronics in Charge
The integration of mechatronics in industrial processes comes with several advantages, including improved efficiency, reduced downtime, enhanced safety, and cost savings. These benefits make it an attractive choice for industries looking to stay competitive in a rapidly evolving world.
Challenges Faced in Mechatronics Integration
Despite its many advantages, the implementation of mechatronics in charge also presents challenges. These may include high initial costs, the need for skilled personnel, and potential vulnerabilities to cyber-attacks.
Future Trends in Mechatronics
The field of mechatronics is continuously evolving. Future trends are likely to involve more advanced sensors, greater automation, and improved human-machine interfaces, further enhancing the role of mechatronics in various industries.
Training and Education in Mechatronics
As the demand for mechatronics professionals grows, educational institutions are offering specialized programs to equip students with the necessary skills. These programs cover a wide range of topics, from mechanical design to software development.
Case Studies: Successful Implementation of Mechatronics in Charge
To understand the real-world impact of mechatronics in charge, let's explore some case studies of its successful implementation in different industries.
How can I apply for admission to MECHATRONICS IN CHARGE
To apply for admission to a program in Mechatronics in Charge, you typically need to follow these steps:
Research Programs: Start by researching institutions that offer Mechatronics in Charge programs. Look for universities, technical colleges, or vocational schools that provide the education you're interested in.
Check Admission Requirements: Each institution may have different admission requirements. These could include prerequisites, standardized test scores, and language proficiency tests (if you're an international student). Make sure you meet these requirements.
Select Your Program: Choose the specific program or course you want to enroll in. Some institutions offer undergraduate degrees, while others may provide diploma or certificate programs in Mechatronics.
Prepare Required Documents: Typically, you will need to prepare the following documents:
High school transcripts or equivalent (for undergraduate programs).
Bachelor's degree and transcripts (for graduate programs).
Standardized test scores (e.g., SAT or ACT for undergraduates, GRE for graduates).
Letters of recommendation.
Statement of purpose or personal statement.
Resume/CV (if required).
Proof of language proficiency (e.g., TOEFL or IELTS for non-native English speakers).
Application Form: Complete the application form provided by the institution. This can often be done online through the institution's website. Be sure to provide accurate information and double-check all details before submission.
Application Fee: Pay the application fee, which is usually required to process your application. Fees can vary between institutions.
Submit Documents: Upload or send all required documents along with your application. Ensure that you meet the application deadline, as late submissions might not be considered.
Interview (If Required): Some programs may require an interview as part of the admission process. Prepare for this by reviewing common interview questions and practicing your responses.
Financial Aid (Optional): If you need financial aid or scholarships, explore the options available through the institution. Some institutions offer scholarships or grants based on merit or need.
Wait for Admission Decision: After submitting your application and all required documents, you'll need to wait for an admission decision. This can take several weeks, so be patient.
Acceptance and Enrollment: If you're accepted, you'll receive an acceptance letter. Review the letter carefully, and if you decide to attend, follow the instructions for enrollment, which may include paying a deposit and registering for classes.
Visa (For International Students): If you're an international student, you'll need to apply for a student visa to study in the country where the institution is located. Be sure to allow ample time for visa processing.
Orientation: Attend orientation sessions provided by the institution to get familiar with campus life, academic requirements, and other important information.
What is the eligibility for MECHATRONICS IN CHARGE
Eligibility requirements for Mechatronics in Charge programs can vary depending on the institution and the specific program. However, I can provide you with some general eligibility criteria that are often associated with such programs:
Educational Background:
For Undergraduate Programs: Typically, you need a high school diploma or an equivalent qualification. It's important to have a strong foundation in subjects like mathematics, physics, and engineering-related coursework.
For Graduate Programs: You usually need a bachelor's degree in a related field such as mechanical engineering, electrical engineering, robotics, or a similar discipline. Some programs may accept students with diverse engineering backgrounds.
Prerequisites:
Some institutions may require prerequisites, which can include specific coursework in mathematics, physics, and engineering fundamentals.
Standardized Tests:
For undergraduate programs, you might be required to take standardized tests such as the SAT or ACT, depending on the institution's policies.
For graduate programs, you may need to provide scores from exams like the GRE (Graduate Record Examination), especially for master's or Ph.D. programs.
Language Proficiency:
If you're a non-native English speaker and plan to study in an English-speaking country, you'll likely need to demonstrate your English language proficiency. This is typically done through tests like TOEFL (Test of English as a Foreign Language) or IELTS (International English Language Testing System).
Letters of Recommendation:
Many graduate programs require letters of recommendation from professors or professionals who can attest to your academic and/or professional abilities.
Statement of Purpose:
A statement of purpose (SOP) or personal statement is often part of the application process. In your SOP, you'll need to explain your reasons for pursuing a Mechatronics in Charge program and your career goals.
Resume/CV:
Some programs may request your resume or curriculum vitae (CV), especially for graduate-level admissions.
Work Experience (for some programs):
Some advanced Mechatronics programs may prefer applicants with relevant work experience in engineering or related fields.
How long does it takes to complete a MECHATRONICS IN CHARGE
The duration to complete a Mechatronics in Charge program can vary based on the level of the program and the specific institution's curriculum. Here are the typical durations for Mechatronics programs at different levels:
Undergraduate Programs:
Bachelor's degree programs in Mechatronics or related fields typically take around 4 years to complete. This duration is standard for most undergraduate programs and includes a combination of general education requirements, core courses, and electives.
Master's Programs:
Master's programs in Mechatronics or a related field typically take around 1.5 to 2 years to complete. The duration may vary depending on whether you are pursuing a Master of Science (M.Sc.) or a Master of Engineering (M.Eng.) degree. These programs typically involve coursework, a thesis or project, and sometimes an internship.
Doctoral (Ph.D.) Programs:
Doctoral programs in Mechatronics are the most advanced level of education in this field. They usually take around 3 to 5 years to complete. Ph.D. programs involve in-depth research, coursework, and the completion of a doctoral dissertation.
What are potential career opportunities after MECHATRONICS IN CHARGE
A Mechatronics in Charge program equips graduates with a unique skill set that combines mechanical engineering, electronics, and computer science. This interdisciplinary knowledge opens the door to a wide range of career opportunities in various industries. Here are some potential career paths after completing a Mechatronics in Charge program:
Mechatronics Engineer: Mechatronics engineers design, develop, and maintain intelligent systems that integrate mechanical components, electronics, and software. They work in industries such as manufacturing, automotive, aerospace, and robotics.
Robotics Engineer: Robotics engineers specialize in designing, building, and programming robots. They work in industries like healthcare, manufacturing, and research, creating robotic systems for various applications.
Automation Engineer: Automation engineers focus on developing automated systems to improve efficiency and productivity in manufacturing and industrial processes. They design and implement control systems for machinery.
Control Systems Engineer: Control systems engineers design and optimize systems to control processes in various industries. They ensure that machinery and processes operate efficiently and safely.
Electro-Mechanical Technician: These technicians maintain and repair mechatronic systems and equipment. They troubleshoot and fix problems in manufacturing, maintenance, and service roles.
Manufacturing Engineer: Manufacturing engineers work to optimize production processes, ensuring that manufacturing systems run smoothly. They focus on efficiency, cost reduction, and quality improvement.
Research and Development (R&D) Engineer: R&D engineers work in labs and research facilities to create innovative mechatronics solutions, pushing the boundaries of technology.
Aerospace Engineer: Aerospace engineers may work on the design and maintenance of aircraft and spacecraft systems, where mechatronics principles are crucial for the control and operation of these vehicles.
Biomedical Engineer: In the field of healthcare, biomedical engineers apply mechatronics to design medical equipment and devices, such as robotic surgery systems and diagnostic tools.
Data Scientist/Engineer: Mechatronics graduates with strong programming skills can pursue careers in data science and analytics, leveraging their knowledge to work on data-driven solutions.
Consultant: Some Mechatronics in Charge graduates choose to work as consultants, helping companies optimize their operations and implement mechatronics solutions for improved efficiency and productivity.
Entrepreneur: If you have a passion for innovation, you can start your own mechatronics-based business, designing and developing custom solutions for various industries.
Academic/Researcher: Pursuing further studies and research in mechatronics can lead to academic careers or research positions at universities, research institutions, or industrial research and development centers.
Maintenance and Service Manager: Graduates can take on managerial roles in maintenance and service departments, overseeing the upkeep of complex mechatronic systems.
Project Manager: Project managers in mechatronics oversee the development and implementation of mechatronics projects, ensuring that they meet specifications and deadlines.
Syllabus of MECHATRONICS IN CHARGE
The specific syllabus for a Mechatronics in Charge program can vary from one institution to another, and it may also depend on the level of the program (e.g., undergraduate or graduate). However, I can provide a general overview of what you might expect in a Mechatronics program, broken down by semesters for a typical 4-year undergraduate program. Keep in mind that course names and content can vary, but the fundamental topics remain consistent:
Semester 1:
Introduction to Mechatronics:
Overview of mechatronics, its importance, and its applications in modern industries.
Engineering Mathematics:
Topics in calculus, algebra, and differential equations relevant to engineering.
Physics for Engineers:
Principles of mechanics, electricity, magnetism, and waves.
Programming Fundamentals:
Introduction to programming languages like C++ or Python.
Introduction to Electrical and Electronic Circuits:
Basics of electrical circuits, components, and electronic devices.
Semester 2:
Mechanics and Dynamics:
Study of statics, dynamics, and kinematics of mechanical systems.
Digital Electronics:
Digital logic circuits, Boolean algebra, and combinational and sequential logic.
Control Systems:
Introduction to control theory and systems.
Materials Science:
Properties of materials, their selection, and applications in engineering.
Mathematics for Engineers II:
Further topics in engineering mathematics, including linear algebra.
Semester 3:
Mechanical Design:
Principles of mechanical design, including CAD (Computer-Aided Design).
Electrical Machines:
Study of electrical machines like motors and generators.
Sensors and Actuators:
Types of sensors and actuators, and their use in mechatronics systems.
Microcontrollers and Embedded Systems:
Introduction to microcontroller programming and interfacing.
Control Systems II:
Advanced control systems and feedback control.
Semester 4:
Digital Signal Processing:
Analysis and processing of digital signals, including filtering and Fourier analysis.
Robotics:
Principles of robotics, including kinematics and programming.
Instrumentation and Measurements:
Techniques and tools for measuring physical quantities.
Advanced Programming for Mechatronics:
Advanced programming skills, algorithms, and data structures.
Industrial Automation:
Automation and control systems used in manufacturing and industrial processes.
Internship opportunities after completing MECHATRONICS IN CHARGE
Completing a Mechatronics in Charge program opens up a range of internship opportunities that allow you to gain practical experience and apply your knowledge in real-world settings. These internships can be invaluable for building your resume, developing industry connections, and refining your skills. Here are some internship opportunities you can explore after completing a Mechatronics in Charge program:
Mechatronics Engineering Intern: Work with mechatronics engineers in various industries, assisting in the design, development, and maintenance of mechatronics systems and devices. This role can provide hands-on experience with sensors, actuators, and control systems.
Robotics Intern: Internships with robotics companies or research labs offer the chance to work on robot design, programming, and testing. You may be involved in projects related to industrial automation, healthcare robotics, or autonomous vehicles.
Automation Engineering Intern: In this role, you'll assist in automating manufacturing and industrial processes. You may work on projects involving control systems, PLC (Programmable Logic Controller) programming, and process optimization.
Electronics Intern: Work with electronics companies to gain experience in circuit design, electronic components, and PCB (Printed Circuit Board) design. This internship can provide insight into the electronic side of mechatronics.
Aerospace Engineering Intern: If you have an interest in aerospace, consider interning with aerospace companies. This can involve working on aircraft systems, avionics, and aerospace control systems.
Biomedical Engineering Intern: Explore internships in the healthcare sector, where you can contribute to the development of medical devices and equipment, such as robotic surgical systems or diagnostic devices.
Manufacturing Intern: Work with manufacturing companies to understand the application of mechatronics principles in the production of consumer goods, industrial machinery, and more. Tasks may involve process optimization and quality control.
Research and Development (R&D) Intern: Join R&D departments of tech companies or research institutions, where you can participate in innovative projects, conduct experiments, and work on cutting-edge technology.
Data Science Intern: Explore data-related internships, where you apply your skills to analyze and interpret data, contributing to decision-making and process improvement in various industries.
Startups: Many startups are developing innovative mechatronics products and solutions. Interning with a startup can provide a dynamic and entrepreneurial experience where you contribute to groundbreaking projects.
Consulting Firms: Internships with engineering consulting firms allow you to work on a variety of projects across different industries, providing exposure to diverse mechatronics applications.
Energy and Utilities: Some companies in the energy sector use mechatronics for control systems in power generation and distribution. Internships in this area offer insights into energy management.
Automotive Industry: Intern with automotive manufacturers or suppliers to work on mechatronics systems for vehicles, including advanced driver assistance systems (ADAS) and autonomous driving technology.
Maintenance and Service Intern: Work with companies that specialize in maintaining and servicing mechatronic systems, gaining hands-on experience in troubleshooting and repair.
Scholarships and grants for MECHATRONICS IN CHARGE
Scholarships and grants for Mechatronics in Charge programs can provide financial assistance to students pursuing their education in this field. These financial aid opportunities can be offered by universities, institutions, government bodies, and private organizations. Here are some potential sources of scholarships and grants for Mechatronics in Charge students:
University Scholarships: Many universities offering Mechatronics programs provide scholarships to incoming students based on academic achievement, leadership, or other criteria. Check with the specific universities you are interested in for details on available scholarships.
Engineering Scholarships: General engineering scholarships may be available to students pursuing degrees in engineering-related fields, including Mechatronics. These scholarships are often offered by professional engineering organizations.
Departmental Scholarships: The engineering or Mechatronics departments of universities may have their own scholarships for students in these programs. Inquire with your department to learn about available opportunities.
Government Scholarships: In some countries, government bodies offer scholarships and grants for students pursuing STEM (Science, Technology, Engineering, and Mathematics) degrees, including Mechatronics.
Private Organizations: Many private companies and organizations, especially those in the engineering and technology sectors, offer scholarships to support students pursuing Mechatronics degrees. These organizations may also provide internship opportunities.
Professional Organizations: Engineering and Mechatronics-specific professional organizations often offer scholarships for students who are members or plan to become members. Examples include IEEE (Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers) and ASME (American Society of Mechanical Engineers).
Diversity Scholarships: Some scholarships specifically target underrepresented groups in STEM fields, including women, minorities, and individuals with disabilities. These scholarships aim to promote diversity and inclusivity in engineering and Mechatronics.
Merit-Based Scholarships: Merit-based scholarships are awarded based on academic achievement, often requiring a high GPA and standardized test scores. These scholarships are typically competitive but can provide substantial financial support.
Need-Based Scholarships: These scholarships are awarded based on financial need. They consider factors such as your family's income and expenses. To apply for need-based aid, you'll typically need to complete the Free Application for Federal Student Aid (FAFSA) or a similar form.
Corporate Scholarships: Some engineering and technology companies offer scholarships as part of their corporate social responsibility initiatives. These scholarships may be tied to future employment with the company.
Rotary Clubs and Community Organizations: Local organizations like Rotary Clubs and community foundations sometimes provide scholarships to students pursuing higher education.
Online Scholarship Search Engines: Utilize scholarship search engines like Fastweb, Scholarships.com, and Cappex to find scholarships tailored to your profile and academic goals.
Conclusion
In conclusion, Mechatronics in Charge is a powerful concept that drives innovation and efficiency in modern industries. It combines mechanical, electrical, and electronic technologies to create intelligent systems that improve productivity and sustainability. As industries continue to embrace mechatronics, we can expect even more remarkable advancements in the years to come.
FAQ,s
What is Mechatronics in Charge?
Mechatronics in Charge refers to the integration of mechatronics principles and technologies into various industrial processes and systems. It involves the use of mechanical components, electrical circuits, and electronic systems to control, monitor, and optimize complex machinery and processes.
What does a Mechatronics in Charge engineer do?
Mechatronics in Charge engineers design, develop, and maintain intelligent systems that combine mechanical components, electronics, and software. They work in various industries, including manufacturing, automotive, robotics, and aerospace, to improve efficiency and automation.
What are the key components of Mechatronics systems?
Mechatronics systems typically comprise three key components: mechanical components (sensors, actuators), electrical components (circuits, wiring), and electronic components (microcontrollers, processors).
What are the educational requirements for a career in Mechatronics in Charge?
To pursue a career in Mechatronics, you usually need at least a bachelor's degree in Mechatronics or a related field, such as mechanical engineering or electrical engineering. Some positions may require a master's or Ph.D. for more advanced roles or research.
What are the applications of Mechatronics in Charge?
Mechatronics in Charge is applied in various industries, including automotive, manufacturing, robotics, healthcare, aerospace, and more. It enhances the performance of machinery and systems in these sectors.
What skills are essential for a Mechatronics engineer?
Mechatronics engineers need a blend of skills, including mechanical design, electronics, programming, and control systems. Problem-solving, analytical thinking, and adaptability are also crucial.
Is Mechatronics in Charge a growing field?
Yes, Mechatronics in Charge is a rapidly growing field, as industries seek to improve automation and efficiency. The demand for professionals with mechatronics expertise is on the rise.
Can I specialize in a particular industry within Mechatronics in Charge?
Yes, you can specialize in areas such as automotive mechatronics, industrial automation, robotics, or aerospace, depending on your interests and career goals.
Are internships common for Mechatronics in Charge students?
Yes, internships are common and highly recommended for Mechatronics students. They provide practical experience and the opportunity to apply classroom knowledge in real-world settings.
What is the typical career path for a Mechatronics in Charge graduate?
Graduates can pursue careers as Mechatronics engineers, robotics engineers, automation engineers, or in related fields. Some may choose to work in research and development, while others may enter industries like manufacturing, automotive, or aerospace.
Are there professional organizations for Mechatronics in Charge professionals?
Yes, there are professional organizations like IEEE (Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers) and ASME (American Society of Mechanical Engineers) that cater to professionals in the field of Mechatronics.
What are the future trends in Mechatronics in Charge?
Future trends in Mechatronics may include more advanced sensors, greater automation, and improved human-machine interfaces, paving the way for even more innovation in various industries.
How can I apply for admission to a Mechatronics in Charge program?
To apply for admission, you typically need to research programs, check admission requirements, prepare required documents, complete an application form, and, in some cases, attend an interview. Be sure to meet application deadlines.
What is the duration of a Mechatronics in Charge program?
The duration can vary based on the level of the program. A bachelor's program typically takes around 4 years, a master's program about 1.5 to 2 years, and a Ph.D. program around 3 to 5 years.
Are scholarships and grants available for Mechatronics in Charge students?
Yes, scholarships and grants are available from universities, government bodies, private organizations, and professional associations to support students pursuing Mechatronics in Charge degrees.